The world of cryptocurrency has witnessed significant growth and evolution over the years, with various consensus algorithms emerging to secure and validate transactions on blockchain networks. Two of the most widely used consensus algorithms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). In this article, we will delve into the world of Proof of Stake, exploring its definition, functionality, and differences from Proof of Work.
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus algorithm used to secure and validate transactions on a blockchain network. It was first introduced in 2011 as an alternative to the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm used in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. In a PoS system, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold, or "stake," rather than their computational power.
In a PoS system, validators are required to "lock up" or "stake" a certain amount of cryptocurrency in order to participate in the validation process. The validator with the largest stake has the highest chance of being chosen to create a new block and validate transactions. This process is designed to be more energy-efficient and less vulnerable to centralization than PoW, as it eliminates the need for powerful computers and high energy consumption.
How Does Proof of Stake Work?
The Proof of Stake algorithm works as follows:
- Staking: Validators deposit a certain amount of cryptocurrency into a wallet or a staking pool, which serves as collateral for their participation in the validation process.
- Selection: The protocol randomly selects a validator to create a new block and validate transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked. The validator with the largest stake has the highest chance of being selected.
- Block Creation: The selected validator creates a new block and adds it to the blockchain.
- Validation: The validator validates the transactions included in the new block and ensures that they are legitimate and follow the rules of the network.
- Reward: The validator is rewarded with a certain amount of cryptocurrency for creating and validating the new block.
How Does Proof of Stake Differ from Proof of Work?
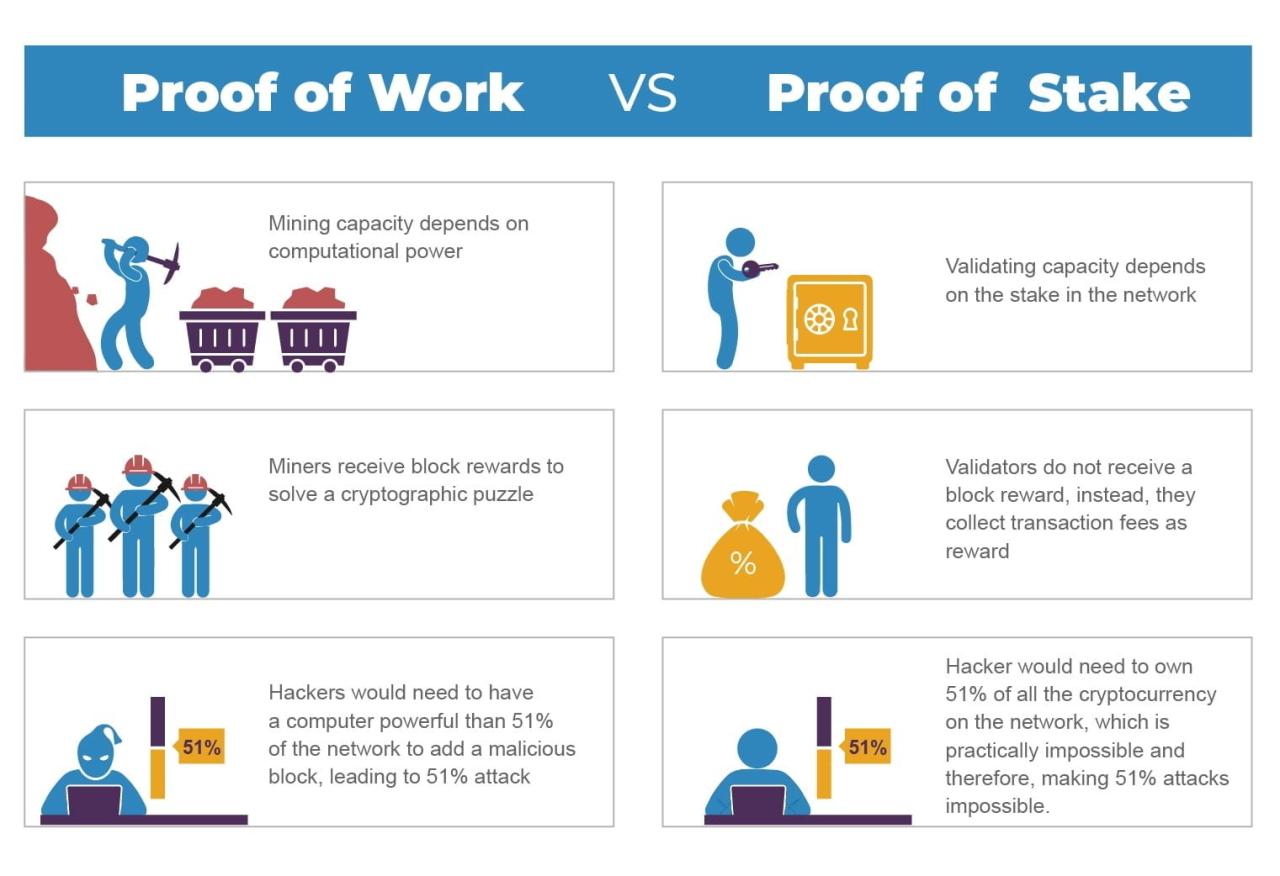
Proof of Stake and Proof of Work are two distinct consensus algorithms with different approaches to securing and validating transactions on a blockchain network. Here are the main differences between the two:
- Energy Efficiency: PoS is more energy-efficient than PoW, as it eliminates the need for powerful computers and high energy consumption. PoW, on the other hand, requires significant computational power to solve complex mathematical equations, which consumes large amounts of energy.
- Centralization: PoS is less vulnerable to centralization than PoW, as it does not require powerful computers and high energy consumption. This makes it more accessible to a wider range of participants, reducing the risk of centralization.
- Security: PoW is considered more secure than PoS, as the energy-intensive process of solving complex mathematical equations makes it difficult for attackers to launch a 51% attack. PoS, on the other hand, relies on the honesty of validators and the security of the underlying protocol.
- Scalability: PoS is more scalable than PoW, as it allows for faster transaction processing and higher throughput. This is because PoS eliminates the need for energy-intensive computations, allowing for more frequent block creation and faster transaction validation.
- Validator Selection: PoW selects validators based on their computational power, while PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked.
Advantages of Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake has several advantages over Proof of Work, including:
- Energy Efficiency: PoS is more energy-efficient than PoW, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
- Increased Scalability: PoS allows for faster transaction processing and higher throughput, making it a more scalable option.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: PoS eliminates the need for powerful computers and high energy consumption, making it more accessible to a wider range of participants.
- Improved Security: PoS reduces the risk of centralization and 51% attacks, as validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked rather than their computational power.
Disadvantages of Proof of Stake
While Proof of Stake has several advantages, it also has some disadvantages, including:
- Nothing-at-Stake Problem: PoS is vulnerable to the nothing-at-stake problem, where validators have an incentive to vote for multiple conflicting versions of the blockchain, as they do not have to spend energy to validate transactions.
- Security Risks: PoS relies on the honesty of validators and the security of the underlying protocol, which can be vulnerable to attacks.
- Centralization Risks: PoS can be vulnerable to centralization risks, as large stakeholders may have a disproportionate amount of influence over the network.
Real-World Applications of Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake has been implemented in various real-world applications, including:
- Ethereum: Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, is planning to transition from PoW to PoS in the near future.
- Tezos: Tezos, a decentralized application platform, uses a variant of PoS called "liquid proof of stake" to secure its network.
- Cosmos: Cosmos, a decentralized network of independent, parallel blockchains, uses a variant of PoS called "tendermint" to secure its network.
- Polkadot: Polkadot, a decentralized platform that enables interoperability between different blockchain networks, uses a variant of PoS called "nominated proof of stake" to secure its network.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Proof of Stake is a consensus algorithm that offers a more energy-efficient, scalable, and secure alternative to Proof of Work. While it has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, PoS has been implemented in various real-world applications and has the potential to play a significant role in the future of blockchain technology. As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how PoS and other consensus algorithms develop and improve over time. With its potential to increase scalability, security, and accessibility, Proof of Stake is an exciting development in the world of blockchain technology.

Leave a Reply