The Ethereum blockchain has revolutionized the way we think about decentralization, cryptocurrency, and smart contracts. However, one aspect of the Ethereum ecosystem that can be a significant hurdle for users is gas fees. In this article, we will delve into the concept of gas fees, how they are calculated, and most importantly, provide you with tips on how to minimize them.
What are Gas Fees?
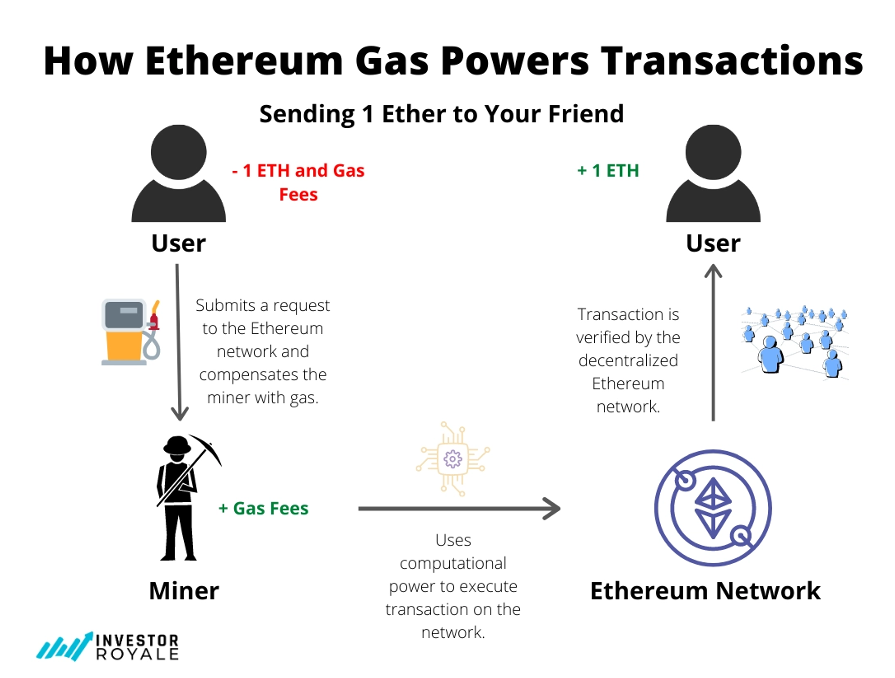
Gas fees are the charges associated with performing transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. Every time you make a transaction, be it sending Ether (ETH) to another wallet, executing a smart contract, or minting an NFT, you need to pay a gas fee. This fee is used to incentivize miners to validate and verify transactions, ensuring the security and integrity of the Ethereum network.
Think of gas fees like the tolls you pay when driving on a highway. Just as tolls support the maintenance and upkeep of the highway, gas fees support the maintenance and security of the Ethereum network. Without these fees, the network would be prone to spam attacks, and miners would have no incentive to validate transactions.
How are Gas Fees Calculated?
Gas fees are calculated based on the amount of gas required to execute a transaction. The amount of gas required depends on the complexity of the transaction. Here are some factors that affect the gas fee:
- Transaction size: The larger the transaction, the more gas it requires.
- Transaction type: Different types of transactions require different amounts of gas. For example, a simple ETH transfer requires less gas than a complex smart contract execution.
- Gas price: The gas price is the price you’re willing to pay for each unit of gas. The higher the gas price, the faster your transaction will be processed.
The gas fee is calculated by multiplying the gas required by the gas price. The unit of measurement for gas fees is Gwei (1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH).
Types of Gas Fees
There are two types of gas fees in Ethereum:
- Base gas fee: This is the minimum gas fee required for a transaction to be processed. The base gas fee is determined by the Ethereum protocol and is currently set at 21,000 gas per transaction.
- Tip: This is an additional gas fee that you can pay to incentivize miners to process your transaction faster. The tip is optional, and you can set it to 0 if you’re willing to wait longer for your transaction to be processed.
Why are Gas Fees High?
Gas fees have been a topic of discussion in the Ethereum community, with some users complaining about high fees. There are several reasons why gas fees can be high:
- Network congestion: When the Ethereum network is congested, gas fees tend to be higher. This is because more users are competing for limited block space, driving up the gas price.
- High demand for block space: When there is high demand for block space, gas fees tend to be higher. This is because miners can choose to prioritize transactions with higher gas fees.
- Limited scalability: The Ethereum network is currently limited in terms of scalability, which means that it can only process a limited number of transactions per block. This can lead to higher gas fees during periods of high demand.
How to Minimize Gas Fees
Minimizing gas fees requires a combination of strategy and timing. Here are some tips to help you minimize gas fees:
- Use gas-optimized wallets: Some wallets, such as MetaMask, allow you to set a custom gas price. This can help you save on gas fees by allowing you to pay a lower gas price.
- Batch transactions: If you need to make multiple transactions, consider batching them together. This can help you save on gas fees by reducing the number of transactions you need to make.
- Use off-chain solutions: Some solutions, such as zk-Rollups and Optimism, allow you to execute transactions off-chain, which can help reduce gas fees.
- Wait for low gas periods: Gas fees tend to be lower during periods of low network congestion. Consider waiting for these periods to make your transactions.
- Use gas-optimized smart contracts: Some smart contracts are optimized for gas efficiency, which can help reduce gas fees.
- Set a custom gas price: If you’re willing to wait longer for your transaction to be processed, consider setting a custom gas price that is lower than the default gas price.
- Use a gas-efficient blockchain: Other blockchain platforms, such as Binance Smart Chain and Polygon, offer lower gas fees than Ethereum.
- Monitor gas prices: Keep an eye on gas prices and adjust your strategy accordingly. You can use tools like Gas Now or ETH Gas Station to monitor gas prices.
Conclusion
Gas fees are an integral part of the Ethereum ecosystem, and understanding how they work can help you navigate the blockchain more effectively. By minimizing gas fees, you can save on costs and make your transactions more efficient. Remember, gas fees are not fixed and can vary depending on network congestion, demand for block space, and other factors. By using gas-optimized wallets, batching transactions, and waiting for low gas periods, you can reduce your gas fees and make the most of the Ethereum network.
Additional Tips
Here are some additional tips to help you minimize gas fees:
- Avoid making transactions during peak hours: Peak hours tend to be between 10am and 5pm UTC, when network congestion is highest.
- Use a gas-efficient token: Some tokens, such as ERC-20 tokens, are optimized for gas efficiency.
- Consider using a layer 2 solution: Layer 2 solutions, such as Optimism and zk-Rollups, offer lower gas fees than the Ethereum mainnet.
- Monitor gas fees regularly: Keep an eye on gas fees and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Use a gas-optimized decentralized application (dApp): Some dApps are optimized for gas efficiency, which can help reduce gas fees.
By following these tips, you can minimize your gas fees and make the most of the Ethereum network. Remember, gas fees are not fixed and can vary depending on a range of factors, so be sure to stay informed and adapt your strategy accordingly.
Leave a Reply