The rise of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) has brought about a new era of innovation and disruption in the financial sector. However, one of the major challenges facing blockchain and DeFi is the need for reliable and trustworthy data feeds, known as oracles. In this article, we will explore the role of oracles in blockchain and DeFi, their importance, types, and how they are revolutionizing the way we interact with smart contracts.
What are Oracles?
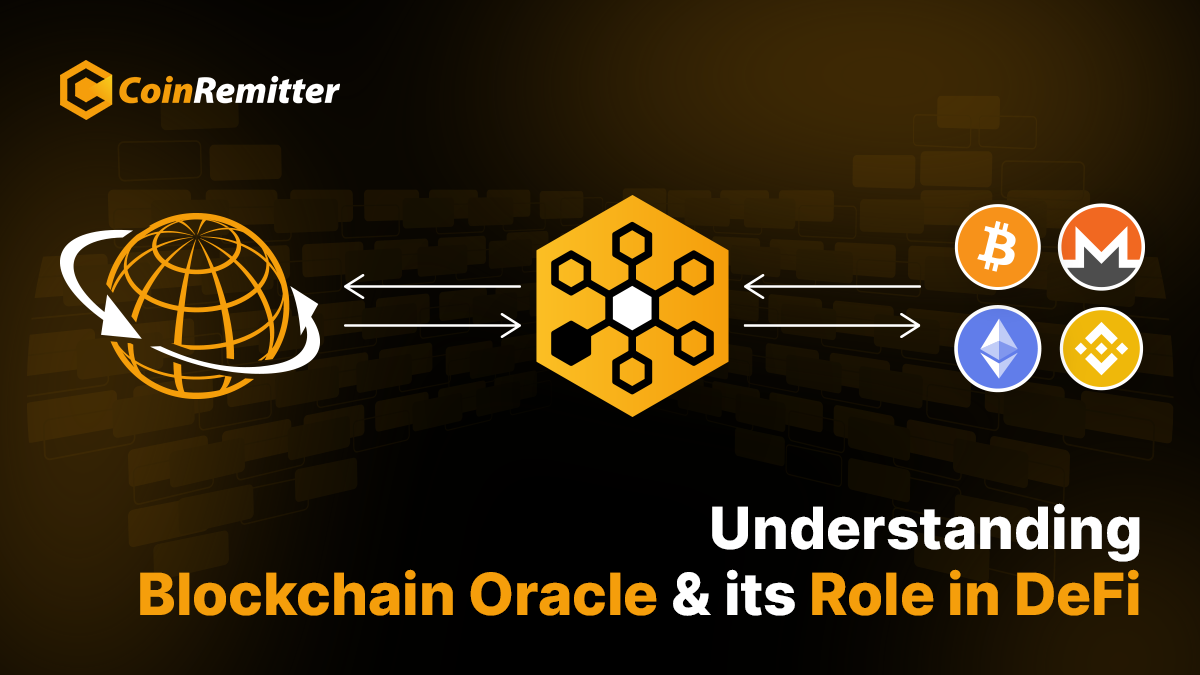
An oracle is a trusted data feed that provides external information to smart contracts on a blockchain network. Oracles act as a bridge between the blockchain and the external world, enabling smart contracts to access off-chain data, such as asset prices, weather forecasts, or sensor readings. Oracles play a vital role in enabling smart contracts to make informed decisions, execute transactions, and settle bets.
The Importance of Oracles
Oracles are crucial for the functioning of DeFi applications, such as lending platforms, stablecoins, and prediction markets. Without oracles, smart contracts would not be able to access external data, limiting their functionality and usefulness. Here are some reasons why oracles are important:
- Enable Smart Contract Execution: Oracles enable smart contracts to execute automatically based on external data, such as asset prices or weather conditions.
- Provide Trustworthy Data: Oracles provide trustworthy data to smart contracts, enabling them to make informed decisions.
- Improve Efficiency: Oracles improve the efficiency of DeFi applications by automating the data feeding process, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Increase Transparency: Oracles increase transparency in DeFi applications by providing real-time data, enabling users to track the performance of their assets.
Types of Oracles
There are several types of oracles, including:
- Software Oracles: These oracles connect to external data sources, such as APIs, to retrieve data and feed it to smart contracts.
- Hardware Oracles: These oracles use hardware sensors, such as GPS or temperature sensors, to collect data and feed it to smart contracts.
- Centralized Oracles: These oracles are controlled by a single entity and are often less secure than decentralized oracles.
- Decentralized Oracles: These oracles are controlled by a decentralized network of nodes and are more secure than centralized oracles.
How Oracles Work
Oracles work by collecting data from external sources, such as APIs or sensors, and feeding it to smart contracts on a blockchain network. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how oracles work:
- Data Collection: The oracle collects data from external sources, such as APIs or sensors.
- Data Processing: The oracle processes the data to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
- Data Transmission: The oracle transmits the processed data to the smart contract.
- Smart Contract Execution: The smart contract executes automatically based on the received data.
Examples of Oracles
- Chainlink: Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides data feeds to smart contracts on Ethereum and other blockchain networks.
- Pyth: Pyth is a decentralized oracle network that provides data feeds to smart contracts on Solana and other blockchain networks.
- Compound: Compound is a DeFi lending platform that uses oracles to determine interest rates and liquidate undercollateralized loans.
Benefits of Decentralized Oracles
Decentralized oracles offer several benefits, including:
- Improved Security: Decentralized oracles are more secure than centralized oracles, as they are less vulnerable to single-point failures.
- Increased Transparency: Decentralized oracles are more transparent than centralized oracles, as they provide real-time data feeds to smart contracts.
- Better Accuracy: Decentralized oracles are more accurate than centralized oracles, as they are less susceptible to data manipulation.
Challenges and Future Directions
While oracles have revolutionized the way we interact with smart contracts, there are several challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some of the challenges and future directions:
- Scalability: Oracles need to scale to support the growth of DeFi applications.
- Security: Oracles need to be secure to prevent data manipulation and theft.
- Interoperability: Oracles need to be interoperable to enable seamless data exchange between different blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Oracles play a vital role in enabling smart contracts to access external data, execute transactions, and settle bets. Decentralized oracles offer several benefits, including improved security, increased transparency, and better accuracy. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed, including scalability, security, and interoperability. As the DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve, the role of oracles will become increasingly important, enabling the creation of more complex and sophisticated smart contracts.
Recommendations
- Developers: Developers should prioritize the use of decentralized oracles to ensure the security and transparency of DeFi applications.
- Users: Users should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of using oracles in DeFi applications.
- Regulators: Regulators should develop guidelines for the use of oracles in DeFi applications to ensure their safe and secure use.
By understanding the role of oracles in blockchain and DeFi, we can unlock the full potential of smart contracts and enable the creation of more complex and sophisticated DeFi applications.
Leave a Reply