The rise of cryptocurrency has led to a significant increase in the number of people investing in digital assets. However, with the growth of the crypto market comes the complexity of navigating taxes on cryptocurrency transactions. The tax laws surrounding cryptocurrency can be confusing, and failure to comply with them can result in significant penalties. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on understanding crypto taxes, how to file them, and avoid penalties.
What are Crypto Taxes?
Crypto taxes refer to the taxes imposed on cryptocurrency transactions, such as buying, selling, trading, or exchanging digital assets. The tax laws surrounding cryptocurrency vary by country, but in general, cryptocurrencies are considered property, not currency, and are subject to capital gains tax.
Types of Crypto Taxes
There are several types of crypto taxes that investors need to be aware of:
- Capital Gains Tax: This tax is imposed on the profit made from selling or exchanging a cryptocurrency. The tax rate varies depending on the investor’s tax bracket and the length of time the asset was held.
- Income Tax: This tax is imposed on the income generated from cryptocurrency transactions, such as mining or staking.
- Self-Employment Tax: This tax is imposed on individuals who earn income from cryptocurrency trading or mining as a business.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): This tax is imposed on the value added to a cryptocurrency transaction, such as buying or selling a digital asset.
How to File Crypto Taxes
Filing crypto taxes can be a complex process, but here are the general steps to follow:
- Keep Accurate Records: Keep a record of all cryptocurrency transactions, including the date, time, amount, and type of transaction.
- Calculate Gains and Losses: Calculate the gains and losses from each transaction, using the fair market value of the cryptocurrency at the time of the transaction.
- Complete Form 8949: Complete Form 8949, which is used to report sales and other dispositions of capital assets.
- Complete Schedule D: Complete Schedule D, which is used to report capital gains and losses.
- Report Income: Report any income generated from cryptocurrency transactions on Form 1040.
Avoiding Penalties
To avoid penalties, it is essential to comply with the tax laws surrounding cryptocurrency. Here are some tips to avoid penalties:
- Keep Accurate Records: Keeping accurate records of all cryptocurrency transactions is crucial to avoiding penalties.
- File on Time: File tax returns on time to avoid late filing penalties.
- Pay Taxes Owed: Pay any taxes owed to avoid penalties and interest.
- Seek Professional Help: Seek professional help from a tax professional or accountant who is experienced in cryptocurrency tax law.
- Stay Up-to-Date: Stay up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations surrounding cryptocurrency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when filing crypto taxes:
- Not Reporting Transactions: Not reporting all cryptocurrency transactions, including small transactions.
- Not Keeping Accurate Records: Not keeping accurate records of cryptocurrency transactions.
- Not Calculating Gains and Losses Correctly: Not calculating gains and losses correctly, using the wrong fair market value or not accounting for fees.
- Not Filing on Time: Not filing tax returns on time, resulting in late filing penalties.
- Not Seeking Professional Help: Not seeking professional help from a tax professional or accountant who is experienced in cryptocurrency tax law.
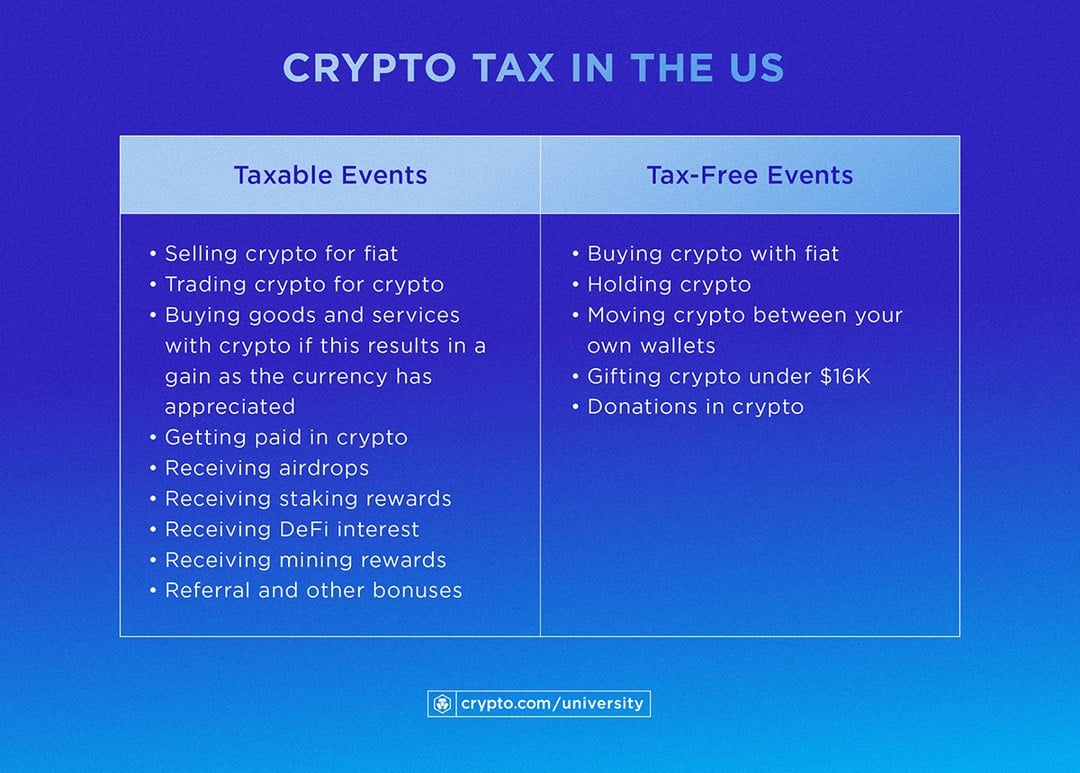
Tax Implications of Different Crypto Transactions
Here are the tax implications of different crypto transactions:
- Buying Cryptocurrency: Buying cryptocurrency is not a taxable event, but the subsequent sale or exchange of the cryptocurrency may be taxable.
- Selling Cryptocurrency: Selling cryptocurrency is a taxable event, and the gain or loss from the sale must be reported on Form 8949 and Schedule D.
- Trading Cryptocurrency: Trading cryptocurrency is a taxable event, and the gain or loss from each trade must be reported on Form 8949 and Schedule D.
- Mining Cryptocurrency: Mining cryptocurrency is a taxable event, and the income generated from mining must be reported on Form 1040.
- Staking Cryptocurrency: Staking cryptocurrency is a taxable event, and the income generated from staking must be reported on Form 1040.
Conclusion
Understanding crypto taxes is essential to navigating the complex world of cryptocurrency investing. By keeping accurate records, calculating gains and losses correctly, and filing tax returns on time, investors can avoid penalties and ensure compliance with tax laws. It is also essential to stay up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations surrounding cryptocurrency and seek professional help from a tax professional or accountant who is experienced in cryptocurrency tax law.
Additional Resources
For more information on crypto taxes, here are some additional resources:
- IRS Website: The IRS website provides information on crypto taxes, including guidance on reporting cryptocurrency transactions and calculating gains and losses.
- Tax Professional or Accountant: A tax professional or accountant who is experienced in cryptocurrency tax law can provide guidance on navigating the complex world of crypto taxes.
- Crypto Tax Software: Crypto tax software, such as CoinTracker or TaxBit, can help investors track and report cryptocurrency transactions and calculate gains and losses.
- Crypto Exchange Websites: Crypto exchange websites, such as Coinbase or Binance, provide information on crypto taxes and may offer tax reporting tools to help investors navigate the tax laws surrounding cryptocurrency.
By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, investors can ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid penalties. Remember to stay up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations surrounding cryptocurrency and seek professional help if needed.
Leave a Reply